What does ATEX mean
What is ATEX? Understand the requirements for proper EX component selection
Tilt down to jump directly to the topics
What does ATEX stand for?
ATEX is a common European standard that sets the requirements for equipment and protective systems used in explosive atmospheres.
The abbreviation comes from the French Explosive atmospheres and covers two EU directives designed to protect people, plant and the environment from the risk of explosion.
In practice, ATEX means that all electrical and mechanical equipment used in potentially explosive environments - for example in chemical industry, refineries, food production or other places with dust or gas - must be designed, tested and documented according to certain safety standards.
ATEX products are often referred to simply as EX products - it means exactly the same thing.
Regardless of the designation, we're talking about solutions that are approved for use in hazardous areas and comply with applicable requirements.
What is the ATEX directive?
The ATEX regulations consist of two directives, each covering a different area:
ATEX 2014/34/EU (Product Directive)
Applies to manufacturers and suppliers of devices. It sets out the requirements for design, testing, labeling and documentation before the product can be placed on the EU marketATEX 1999/92/EC (Work Directive)
Applies to employers who must ensure the safe use of equipment in explosive atmospheres. It's about zones, risk assessment, operation and maintenance
Both directives are closely linked - and it is only when the equipment is approved and used correctly in relation to the zones that safety is fully met.
When does ATEX apply to your business?
ATEX regulations apply to companies where an explosive atmosphere can occur in the workplace. This means situations where air is mixed with flammable substances such as gas, vapor, mist or dust, and where ignition can lead to an explosion
The requirements come into effect when a workplace assessment shows that potentially explosive zones are present. The company must then implement the necessary technical and organizational safety measures
ATEX includes among others:
- Businesses with Ex zones, e.g. where flammable liquids, gases or dust such as grain, flour, wood dust or chemicals are handled
- Equipment and installations used in these areas - both electrical and non-electrical (ATEX 114/formerly 95)
- Employer's responsibility for occupational health and safety and employee protection, including zone classification, APV and instruction (ATEX 137/1999/92/EC)
What is an ATEX zone?
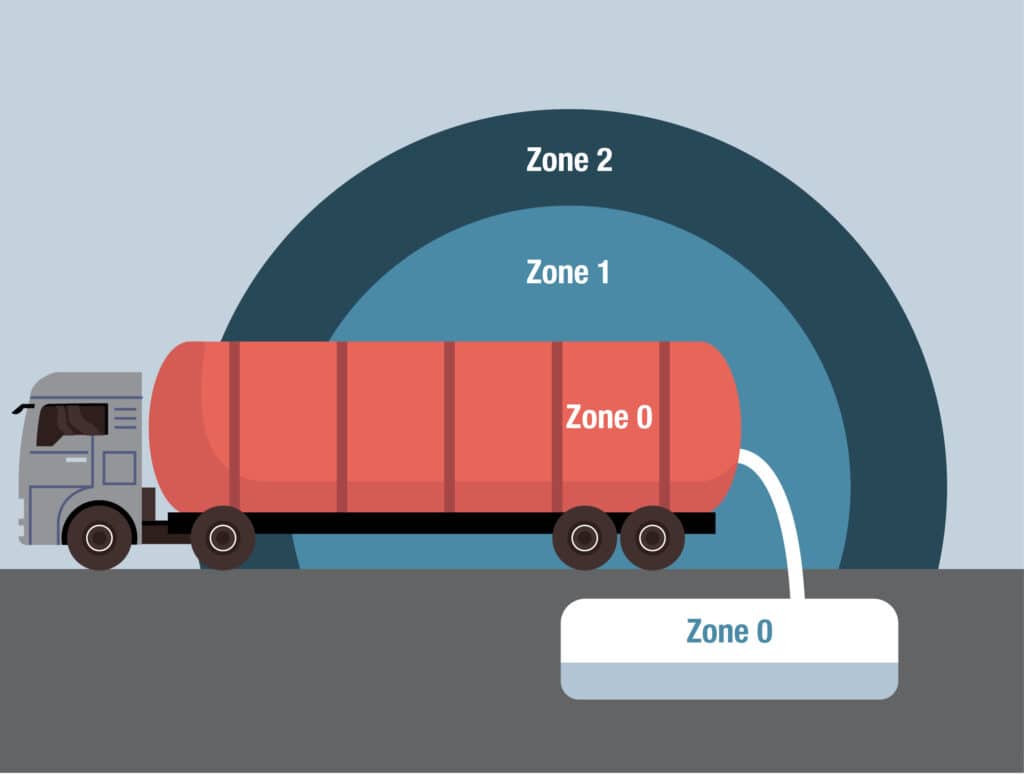
Zone 0, 1 and 2 (gas)
Gas zone classification is used in areas where explosive gas atmospheres may occur.
- Zone 0: Areas where an explosive gas atmosphere is present continuously, for long periods or frequently
- Zone 1: Areas where an explosive gas atmosphere is likely to occur during normal operation
- Zone 2: Areas where an explosive gas atmosphere does not normally occur during normal operation and if it does occur, will only be present for a short time
Zoning is used to select the correct ATEX-approved equipment and ensure installations meet applicable safety requirements.
Zone 20, 21 and 22 (dust)
Zone classification for dust applies in areas where explosive dust atmospheres can form.
- Zone 20: Areas where an explosive dust atmosphere is present constantly, for long periods or frequently
- Zone 21: Areas where an explosive dust atmosphere is likely to occur during normal operation
- Zone 22: Areas where an explosive dust atmosphere does not normally occur during normal operation and if it does occur, will only be present for a short time
Dust zones are typically found in silos, mills, food production and wood industries where fine dust can accumulate and ignite.
How is zone classification done?
Zone classification is done through a systematic risk assessment of the facility and work area. The process typically includes:
- Identification of hazardous substances - e.g. flammable gases, vapors or combustible dust
- Assessment of spills - Where, how often and in what quantities can the substance be released?
- Ventilation conditions - Natural or mechanical ventilation has a major impact on the extent of the zone
- Duration and frequency - How long and how often can an explosive atmosphere occur?
- Documentation - The results are compiled in an ATEX documentation with zone plans and technical descriptions
The zone classification must be carried out by professionally competent persons and form the basis for choosing the correct equipment, installation and preventive measures. We can help refer you to companies that perform classification.
How to know the ATEX zones
We have a wide range of ATEX approved products for zones 1 & 2 (gas) and zones 21 & 22 (dust).
To the left is an example of what the ATEX zones look like for a tanker truck with e.g. gas.
What to look for
- The EX symbol
- Manufacturer's name, registered trade name or registered trademark and address
- CE marking and number of the notified body involved
- Series and type designation
- Batch or serial number if applicable
- Year of manufacture
How to read an ATEX marking
Deciphering whether a component has the right ATEX approval can be complicated.
Here we guide you through what a typical ATEX marking might look like.
Example:
II 2G Ex eb IIC T6 Gb:
- The ATEX mark (EX icon)
- II: Equipment group II - above ground use (not mining)
2G: Category 2 - gas (suitable for areas where explosive gas atmospheres may occasionally occur - Zone 1)
Ex eb: Type of protection - increased safety (”e” = increased safety, protection level b)
IIC: Gas group (the most demanding gas group, e.g. hydrogen and acetylene)
T6: Temperature class (maximum surface temperature 85 °C)
Gb: Equipment Protection Level (EPL) for gas - high protection level, suitable for Zone 1

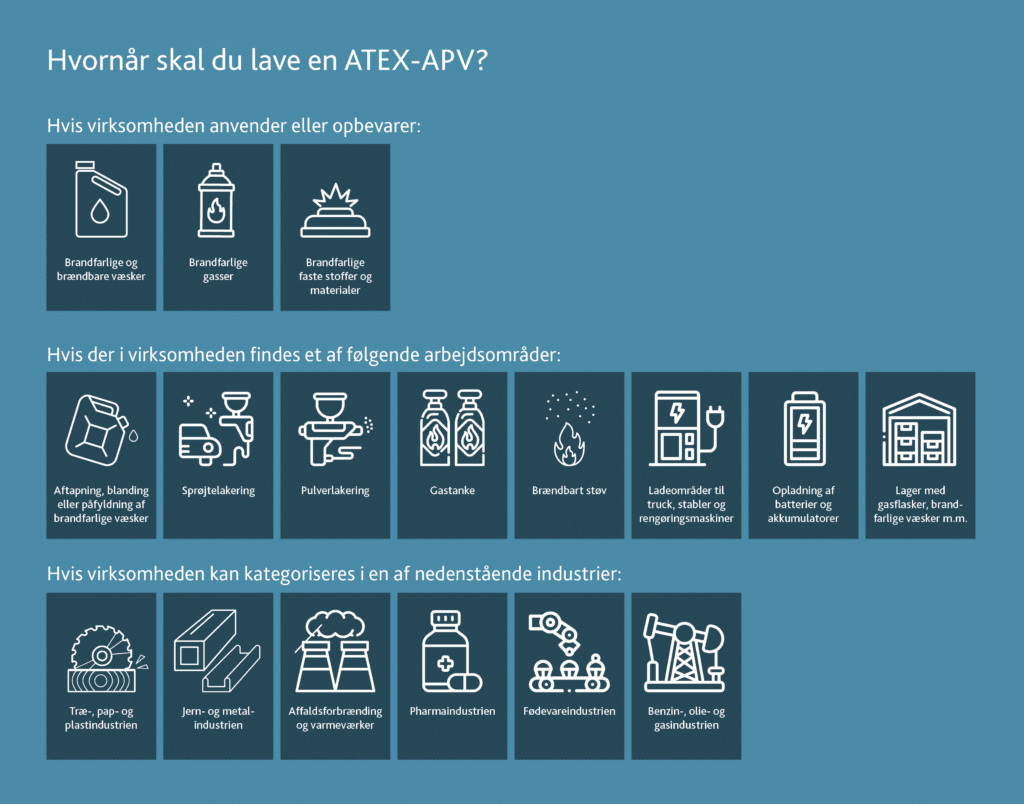
ATEX-APV - when is it mandatory?
An ATEX-APV is required by law when there may be a explosive atmosphere in the workplace. This applies when working with flammable gases, vapors, mists or dusts that can ignite.
The ATEX APV must be part of the company's regular workplace assessment (APV) and must be prepared, before starting work - and updated in case of changes in work processes, substances or equipment.
The purpose is to document that the risk has been assessed and managed correctly so that employees are protected against explosions.
What should an ATEX APV contain?
The ATEX-APV must as a minimum describe:
- Where and when explosive atmospheres can occur
- Explosion risk assessment
- What measures prevent an explosion
- Classification of hazardous areas (zones)
- What equipment can be used in the classified areas
High-quality ATEX products are always a pleasure

Martin and Sune inspect Moxa's NGate, which is ATEX certified for use in classified zones.
How we work with ATEX at Thiim
At Thiim, we are experts in ATEX and focus on ATEX products and ATEX-approved products for installations in hazardous areas.
- Our team has completed ATEX training at Machine Safety and has specialized knowledge of the requirements for products in zones 1/2 and 21/22
- We work across industries with high demands on documentation, safety and quality
- We are experiencing increasing attention from both authorities and insurance companies on the correct use of ATEX-approved products - and here we stand strong with documented competence and in-depth product knowledge
- From classic electrical components such as switches, control boxes and CEE connectors to ATEX approved industrial IT solutions such as switches, panel PCs and routers
- We have prioritized suppliers with high quality, certified documentation and a broad ATEX program
ATEX is not just a product category for us - it's a specialty area. We continuously improve our skills and ensure that our ATEX expertise is always up-to-date and relevant to market requirements.
Typical mistakes companies make with ATEX
Many companies underestimate the bigger picture of ATEX, especially when projects are pressed for time or handled as a “standard installation”. The result is often wrong choices in the design phase that are only discovered during audit, commissioning or - worse - operation.
ATEX requires holistic thinking: zone classification, temperature classes, equipment categories, documentation and proper installation must be connected.
Below are examples of the most common errors we encounter in practice
- Choosing the wrong protection type (Ex d, Ex e, Ex i, etc.)
- Overlooks that dust can be flammable
- Failure to consider ambient temperature
- Incorrect or non-certified cable entry
- Oversized or unnecessary category 1 equipment
- Confusion between IECEx and ATEX (certification vs. directive requirements)
- Missing or incorrect zone classification
- Wrong temperature class (T-class) in relation to gas/dust
- Insufficient documentation
- Failure to assess mechanical ignition sources
- Incorrect equipotential bonding/grounding
- Use of standard components in ATEX enclosures without overall approval
- Lack of maintenance and inspection plan according to EN 60079-17
- Changes to the installation without updating the risk assessment
ATEX errors rarely occur out of ignorance - but because responsibilities, interfaces and documentation are not clearly defined from the start.
If you have an ATEX environment or a project underway, we are happy to help with the correct choice of components, protection type and documentation - ensuring that the solution is both technical and optimal throughout the project.
FAQ about ATEX and explosion protection
Is ATEX mandatory?
What it is. ATEX is required by law in Denmark and the rest of the EU when explosive atmospheres can occur in the workplace. Employers have a duty to assess the risk and ensure that both installations and equipment comply with the ATEX directives.
What is the difference between IECEx and ATEX?
ATEX is the European legislation that applies in the EU.
IECEx is an international certification scheme.
ATEX is a legal requirement in the EU, while IECEx is typically used when exporting outside the EU. Many products are certified according to both schemes.
When should you do an explosion risk assessment?
An explosion risk assessment (ATEX-APV) must be carried out when an explosive atmosphere may occur - for example when working with flammable gases, vapors or combustible dust.
It must be prepared before work starts and updated if there are changes in processes, materials or installations.
Who can perform ATEX installations?
ATEX installations may only be carried out by qualified and competent professionals with knowledge of applicable regulations and standards. Electrical installations in ATEX zones must be carried out by authorized electrical installers with documented ATEX competence.
What is an ATEX zone?
An ATEX zone is an area where explosive atmospheres can occur.
Areas are typically classified as:
- Zone 0, 1, 2 (gas)
- Zone 20, 21, 22 (dust)
The zone classification determines which ATEX equipment can be used.
What is an ATEX APV?
An ATEX WPV is a workplace assessment that documents the risk of explosion and describes how to manage it. It is required by law if there is a risk of an explosive atmosphere.
What happens if you don't comply with ATEX regulations?
Non-compliance may result:
- Orders from the Danish Working Environment Authority
- Fines and penalties
- Downtime
- Increased liability in accidents
In addition, it can have serious safety implications.
Does all equipment in an ATEX zone need to be ATEX approved?
Yes. All electrical and mechanical equipment in a classified ATEX zone must be approved for the specific zone. Incorrect equipment can be both illegal and dangerous.
Does ATEX only apply to the chemical industry?
Answer. ATEX applies to all industries where explosive atmospheres can occur - for example
- Food production (flour and dust explosions)
- Agriculture and biogas
- Wood industry
- Pharma
- Metal industry
Who can clarify if I have ATEX zones?
Classification of whether a company is covered by the ATEX regulations, as well as zone classification, must be carried out by competent persons with specialized knowledge of explosion risks, applicable directives and relevant standards.
It is always the employer's responsibility to ensure that an explosion protection document is available. In practice, however, the technical assessment and classification is often carried out by external specialists with the necessary professional expertise. There are several skilled experts in this field.
How do I know which ATEX equipment to choose?
It depends on:
- The zone classification
- Temperature class
- Gas or dust type
- How to use the equipment
The choice should always be based on the company's ATEX-APV and zone plan.
We deliver ATEX-approved solutions in uncompromising quality.
We offer a strong range of proven ATEX electrical components and robust products for industrial IT in hazardous environments.
Can't find exactly what you're looking for?
Contact us - we'll get the right solution.
